Well, your business has grown enough to expand the boundaries or, probably, you’re starting as a global business or service provider. So you came to the idea of creating language/country-based versions of your website to target users in the new markets. A daunting task that will make you look at international markets and dive into all things international SEO.
A daunting task I said, but in fact not that daunting, if you gear up and have a plan. Well, let’s do things in the right order.
What’s international SEO?
International SEO helps you deliver content in multiple languages to users (and search engines!) in different locations. It also ensures that specific content is shown to users depending on their location or spoken language. Though international and “regular” SEO share the basics, they require different approaches and tactics. International SEO involves a deeper understanding of all things technical and requires some preparatory work to be done.
Thus an international SEO implementation plan may include steps as follows:
Assess your international readiness
Fundamentally, going global requires sufficient groundwork. The same is the case for international SEO. So before launching an international SEO campaign, you need to balance your expectations and abilities. This will help you get a clearer picture of what this step will cost you in terms of money, time, and resources. To define whether your business is ready to take this step, answer some questions:
- Are you ready to create a different user experience, specific to users of different regions/languages?
Going global doesn’t mean just translating your site to a new language. You need to build up a specific user experience that takes into account your international users’ spoken language, culture, and the peculiarities of the targeted market. - Are you able to create, review, and maintain content aimed at users of different regions/languages?
Simply creating content for each language/country-based website version is not enough. You should be ready to maintain it and keep it up to date. Will you be able to handle this using your own resources? Probably, you’ll require additional hands. What then would suit you better: expanding your onsite team or having a dedicated team in your targeted region? - Are you ready to support customers in a new region/language?
The international expansion brings you more customers. It also brings the necessity to provide quality customer support. Which means you’ll need people in your support team speaking corresponding languages and being available to customers from different time zones.
Answering these questions may show you the real picture of what to expect in terms of necessary investment and additional staff size. It may also influence the choice of international SEO tactics and tools.
Identify potential markets to target
Unless your business initially targets different regions worldwide, you come to think about doing international SEO when you start seeing a sufficient foreign customer flow. Analyzing this flow will help you identify the potential market to target.
There’s a great instrument you can use to evaluate your traffic. I’m talking about Google Analytics. It gives you the possibility to analyze the overall traffic your website receives from different countries. You can also evaluate each country’s traffic from the commercial point of view, analyzing the number of transactions, revenue and other factors that may hint you at the market potential.
Simply open your Google Analytics account and go to Audience>Geo>Location or Language. Now you may analyze the data:
- Are there any visits to your site from other countries?
- What languages do they speak?
- Does any country send more traffic to your site than others?
- Traffic from which country already converts, etc.?
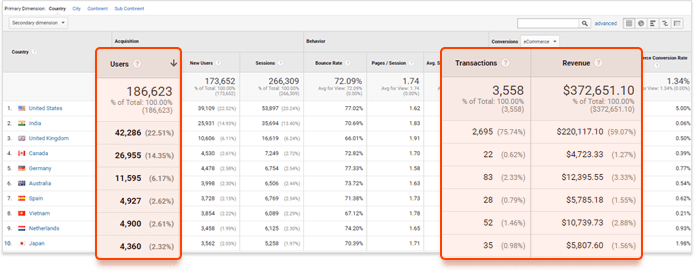
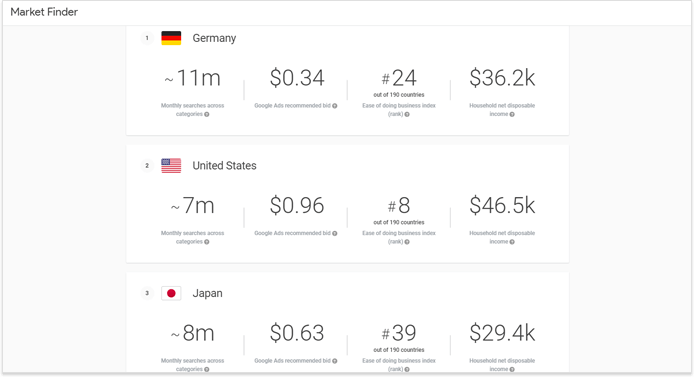
There’s another way to search for potential markets using, for example, tools such as Google’s Market Finder. Basically, it may be an additional instrument to check for opportunities by evaluating the overall interest in your business or service(s) you provide.
All you need is to enter your URL and let the tool analyze your website. It then will automatically pull categories for your website — you’ll have the possibility to correct them — and show you the markets that may potentially interest you.
Do separate keyword research for each website version
The primary goal of SEO is to make your website show up in SERP(s) for the keywords you target. This is the basic element international and “regular” SEO have in common. So in terms of keyword research mechanics, there will be nothing totally different. There’s a great guide on keyword research that you can read for more details. However, it’s critically important to do separate keyword research for each country or language-based site version. Here’s why:
1. Translated keywords are not the search queries people use in real life. Clearly, you can’t just translate the list of target keywords you have for your main website version and use it to optimize your foreign-language site. Because translated keywords may differ greatly from the real search queries people use.
2. Even the same language in different countries has its peculiarities. Though people living in different countries may officially speak one language, in reality, they speak different variants of the same language. So they may search for the same things using different queries.
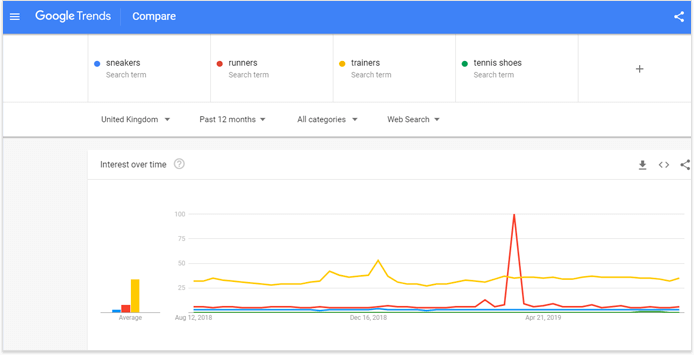
Let’s take for example the word “sneakers“. If we’d need to define sneakers in general, we’d say they are rubber-soled sports shoes. People love sneakers, they are extremely popular footwear. In the US.
But in the UK for example, people search for the same rubber-soled shoes calling them “trainers“. I’ve seen also “runners”, “tennis shoes” and a couple of other names meaning relatively the same type of footwear.
And if we check how people in different English speaking countries search for this footwear, we’ll see an interesting result that Google Trends show, for example.
This is the result for the United States. People are largely interested in “sneakers“:
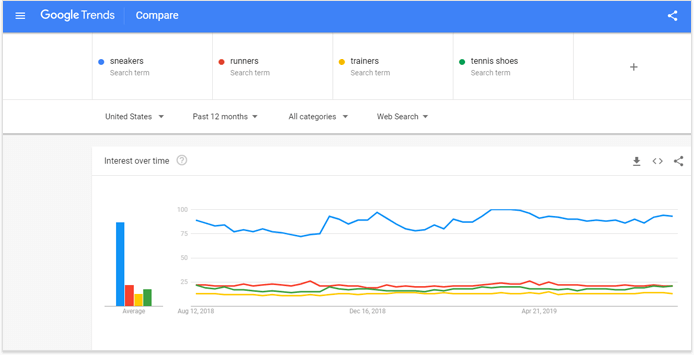
But look at the result from the United Kingdom. As you can see, there’s a vast interest in “trainers” instead.
Analyze and leverage the competition
Now, once you have defined potential markets to target, it’s time to make a second step and scan the competitive landscape. It doesn’t matter what strategy you choose for your international SEO campaign, you simply can’t go without thorough competitive analysis.
Important note. The biggest mistake one can make at this stage is to get the wrong picture if analyzing the wrong SERPs. You definitely know that search results differ depending on the searchers’ location. So people in the UK and the US searchers will see different results for the same search query. Thus it’s critical to perform competitor research and analyze local SERPs from the right location.
So how can competitors research power your international SEO?
1. It gives the real picture of who you compete with on the local search market.
No need to say that there may be a huge difference between your offline and online competitors. You might know the biggest players in your target market niche. But not necessarily the same companies will appear to be your SEO competitors.
So finding who outranks you in SERPs for your target keywords may greatly influence what tactics to prioritize doing SEO in this market.
- First, you enrich your keyword list with great keywords people in your target market use to search for things.
- Second, analyzing the keywords’ difficulty scores and competition you may prioritize what keywords to target.
- And third, analyzing your own positions for the competitors’ ranking keywords, you may find those, you’re in striking distance from the first SERP. So you’ll know for sure where to put your effort into.
3. It hints you at your competitors’ successful SEO tactics. Knowing what works well for your competitors, you may use it in your own SEO campaign. In fact, this saves loads of time and resources. And this is especially handy when you’re not sure what to put your effort into.
Work on the technical side
Going global needs a great deal of technical work done right in order to succeed. The majority of issues that affect international SEO are connected with the technical part. Thus it’s critical to do things the right way. So let’s see what is important here.
Choosing the domain and website structure
URLs optimized for language and region is one of the signals search engines take into account in local ranking. So choosing the right domain is a crucial point in an international SEO campaign. There are several options, each having its pros and cons. So you may choose what better suits your goals and possibilities.
- Country-coded top-level-domains (ccTLD) — www.example.uk (or www.example.co.uk).
This domain type is believed to be a strong signal pointing to Google on the audience and country it aims at. Choosing this domain usually comes together with choosing local hosting. However, it is very expensive in maintenance. So it can make sense in case you are targeting a country where people speak one certain language. Or if there are legal requirements for ccTDLs to run a business on the market. - Subdomains — www.uk.example.com.
This domain type allows for creating multiple languages or country instances to target users in certain markets. However, a subdomain will still require a separate SEO done from scratch. - Subdirectories — www.example.com/uk/.
Subdirectories are the easiest option to implement and maintain, you just create another folder on your website. The great advantage of such domain types is that they inherit the ranking value of the root domain. At the same time, you can track them separately in Google Analytics and Google Search Console.
Setting up Hreflangs
But the most powerful thing that signals to search engines about what audience a website version targets, in terms of languages and (or) location is an hreflang attribute.
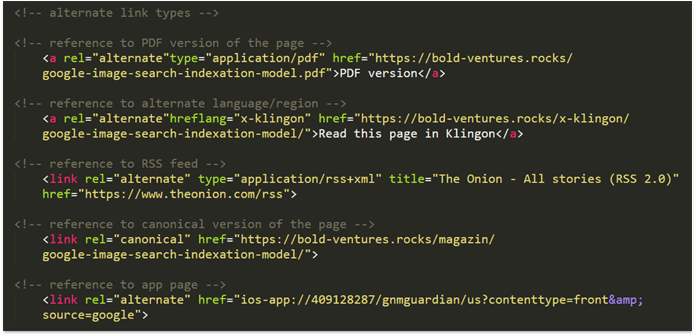
Hreflangs are hyperlink references for a specific language, multiple regions with the same language, or one region with multiple languages a webpage targets.
The hreflang attribute may be implemented in 3 different ways: in the <head> section of a page, in XML sitemaps, and in the HTTP Header for non-HTML files.
In the code, the attribute looks like this:
<link rel="alternate" href="https://domain.uk/" hreflang="en–GB" />
Let’s define what parts this piece of code includes. This will help understand how Hreflangs work.
The href= element contains the alternative page’s URL;
The hreflang= element indicates the language or the language and country the alternative URL targets.
Hreflangs work really well when they are implemented correctly. But it’s quite challenging. The most common issues that arise when implementing Hreflang are as follows:
- Different versions of a page are nested under one ccTLD.
- Wrong ISO code is used in the hreflang annotation.
- Hreflang indicates a region only.
- Hreflang’s pointing to relative URLs.
- Hreflang blocked by mistake, and more.
All these issues are bewildering search engines, leaving them unaware of what content to serve to this or that audience. Getting to know how to set up hreflangs is then really indispensable.
Localize your content
Almost the last but not the least. The content of your website. Your most valuable asset you want users to have access to. And you need to approach your internationally targeted content taking into account not only the language your users speak but cultural differences and peculiarities of the market. So definitely, simply translating your website to a corresponding language is not an option. Instead, you need to localize it with respect to language and cultural peculiarities of your users.
In fact, localization may go quite smoothly, if you know the challenges you may face:
The lack of local staff. There’s a controversy about whether you really need a localization team in your target region. Well, the answer is, it depends. Expanding your team is a costly option, so in case of a limited budget, you’ll be tackling it using your own forces. However, having local staff has its advantages.
- They are more aware of the peculiarities of the market and may suggest better working things like keywords, slogans, etc.
- They speak the same language as your target audience does, while your in-house staff even speaking a certain language may be unaware of all things little variations and commonly used phrases.
Inconsistency across the localized content. It’s a common challenge that occurs when a distributed team works on localization. There may be terms that can be translated in different ways. And this may bewilder users, which is bad in terms of user experience. So the best practice that works very well is to create a glossary of important terms and encourage the localization team to stick to it.
Poorly optimized content. The thing is, even a high-quality localized content may poorly rank for your target keywords if it’s not optimized for them. So you need to elaborate content optimization rules for your localization team to follow. And you may leverage content optimization platforms to ensure a more creative and fruitful content optimization process.
Build quality backlinks
Backlinks are still one of the most significant ranking signals. At the same time, link building is an often overlooked part of an international SEO strategy. This happens due to different reasons — from the lack of resources to prioritizing other tactics, like content optimization, etc. But in fact, international SEO is a big separate project, in which no part can be omitted if you strive for success. So let’s look at what link building tactics may power an international SEO strategy.
Leverage the main website backlinks profile. Normally, if your website receives foreign traffic, there is a big chance you have international links pointing to your main website. Analyzing your backlink profile will help you define such links. So you’ll just need to outreach website owners and ask them to link to your site version that is more relevant for their users. In fact, it’s a win-win, as the website owners provide better user experience, and you get quality links.
Think beyond Google
Though Google is the most used search engine in the world, there are alternative popular search engines in different regions. So it would be quite unwise to miss out on the opportunities they provide. So let’s see what search engines, apart from Google, rock in different regions worldwide.
Europe — Bing is the second most popular search engine in the world. And it’s widely used in Europe, especially in the UK and France where it takes 4% and 2,8% of the market share respectively.
Russia and the Russian speaking countries — Though Yandex gets about 1% of the worldwide search market, in Russia and the Russian speaking region it beats Google. The share of Yandex in the Russian search market reaches up to 48%, while the share of Google is about 47%.
China — China has a bunch of its own search engines, with Baidu as a leader. Here Google is the most unpopular option (and it’s been, in fact, banned from the Chinese market).
Conclusion
Thinking about international SEO as a general SEO side-project is quite unlikely to lead you to any success. It’s more likely to have you spend time and money for no or very insignificant result. So if you believe it’s time to go global, make international SEO an important independent project you are ready to invest money, time, and resources into. Double-check your readiness, define what parts of the process your team will be responsible for, and what you’ll assign to a local team. Prepare a plan and stick to it.
Looking to build customer loyalty through social media? Don’t forget to add your business to Top4 Marketing
List your business, create your own digital store to sell goods and services, and share posts on social media. Promote your business on Google instantly! Should you need help with local digital marketing then view our new Google Marketing Platform and services Top4 Marketing
Get Found On Google Promote Your Website, Reach local customers today!
Our Digital Marketing Agency Services Across All Industries Include Search Engine Optimisation (SEO), Google Marketing, Website Design, Corporate Web Development, and local location-based marketing using our own Google Marketing Platform!
Engage A Social Media Agency For Only 1/3 The Cost Of Employing A Social Media Manager…LET’S TALK!
Source: Link Assistant





